Pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) has become an accepted therapeutic strategy for AF.1 The cryoballoon (CB) ablation system has been introduced into clinical practice as a tool for a single-shot anatomical based-PVI, and a comparable efficacy of the CB ablation to radiofrequency (RF) ablation has been demonstrated in a prospective randomised study.2–4
The recently introduced second-generation CB (Arctic Front Advance, Medtronic) has become the standard tool owing to the greater cooling effect and higher efficacy when compared with the first-generation CB.5,6 However, this also raises concern of collateral damage to non-cardiac structures. Several recent studies have shown that the enhanced cooling effect successfully reduced the freezing interval to 180 seconds (single freeze) or time-to-isolation of the guided-strategy, and eliminated the bonus freeze without a reduction in long-term efficacy.7–10 This article focuses on the representative complications in second-generation CB ablation procedures.
Phrenic Nerve Injury
CB ablation is associated with a significant risk of phrenic nerve injury (PNI) due to the limited balloon size, and right PNI is the most common complication in the CB ablation procedure.3–6,11 The reported incidence of PNI varies owing to different definitions (of PNI), balloon generations (first or second), balloon size, freezing regimen and protective manoeuvres. Currently, continuous monitoring of the diaphragmatic compound motor action potentials (CMAPs) has become an accepted technique in clinical practice, which involves freezing being immediately terminated with a double-stop technique, active deflation, when the CMAP significantly decreases.12–15
We looked at the incidence and characteristics of PNI in 550 AF patients who underwent PVI using one 28 mm second-generation CB and a single 3-minute freeze strategy under CMAP monitoring.16 A total of 34 (6.2%) patients experienced PNI during the right superior pulmonary vein (RSPV; n=30) and inferior PV ablation (n=4). However, no patients experienced left PNI. Applications were interrupted using double-stop techniques after median 136-second (25–75th percentile: 104–158) applications, and a PVI was already achieved in all but one case. Persistent AF, larger RSPV ostia, and deeper balloon positions on fluoroscopy were associated with higher incidences of PNI. The incidence of PNI during the procedure, and 1 day and 1 month afterwards was 6.2%, 2.4%, and 1.6%, respectively. All PNI was asymptomatic and reversible during the follow-up period. The CMAP amplitude during the emergent deflation predicted the delay in the PNI recovery, and all incidents of PNI recovered by the next day in patients with a remaining CMAP amplitude of >0.2 mV.
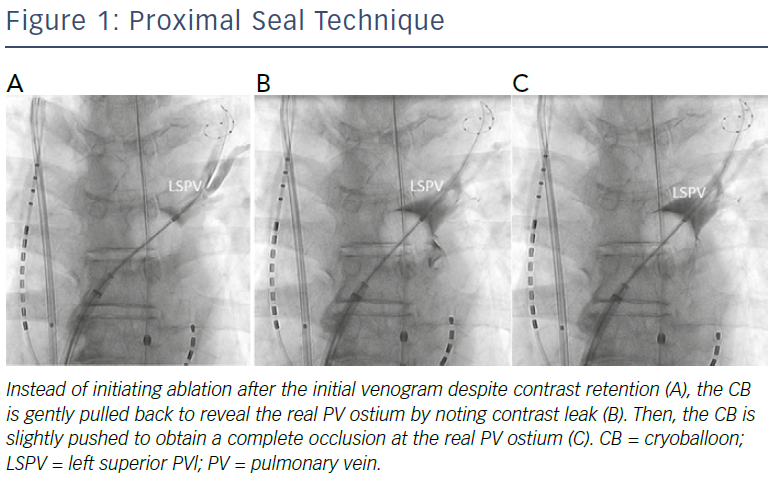
These data suggest that early recognition of CMAP amplitude reductions and immediate active deflations appear to be essential for early recovery from PNI. The key to minimising the risk of PNI is to ensure the balloon position is as antral as possible, and for this purpose, a proximal-seal technique (Figure 1) is recommended to avoid any deep CB positioning.6 If no leak is visible on venography, withdraw the CB slightly and allow a leak around the PV–balloon interface to better define the PV ostium and ensure a proximal ablation. Then, reapply only the minimal amount of pressure needed to regain the occlusion before the ablation. Since the CB size becomes slightly larger when the freezing starts, a small leakage is generally sealed by the CB applications. However, it should be noted that PNI could occur even when the balloon position is proximal, presumably because the phrenic nerve course varies among patients. Therefore, careful CMAP monitoring is mandatory during applications regardless of the RSPV size.
Obtaining a stable position of the pacing catheter is important given that catheter dislodgement also results in a decrease in the CMAP amplitude. Pacing should be continued during the initial thawing time because PNI could occur during that period.16 Since this complication is usually asymptomatic, a chest X-ray is recommended before the procedure and on the next day. PNI is almost always asymptomatic and reversible during the follow-up period if the procedure was carefully performed, thus PNI is the most common, but is not a serious complication in the CB ablation procedure.
PV Stenosis
PV stenosis has been a well-recognised complication of AF ablation regardless of the use of the energy sources.1,17 Moreover, there are data showing a progression of stenosis during the 3 months after RF ablation.17 The reported incidence of PV stenosis could differ due to different ablation techniques, definitions of PV stenosis, and intensity of the screening for this complication. Generally, it is believed that cryoablation has a lower risk of PV stenosis due to tissue shrinkage when compared with RF ablation because of the preservation of the basic underlying tissue architecture with preserved endocardial contours and minimal cartilage formation after the ablation.18 Since PV stenosis has not been evaluated with adequate modalities in the vast majority of centres, the reported data is limited. A few have revealed that first-generation CB ablation could result in PV stenosis and that a longer application time and use of a 23 mm CB increased the risk of this complication.3
Severe PV stenosis has also been reported after the introduction of the second-generation CB.19,20 We investigated 276 patients who underwent CB PVI using one 28 mm balloon with a single 3-minute freeze strategy.21 If the balloon temperatures reached −60°C or PNI was suspected, freezing was terminated. Enhanced cardiac CT was obtained before and >3 months after the procedure. Follow-up CT obtained at a median of 5.0 months post-procedure revealed no PVs with moderate (50–75%) or severe (>75%) stenosis. Asymptomatic mild stenosis (25–50%) was documented in 16/1,101 (1.4%) PVs, but did not progress during the follow-up period.
These results are presumably because the applications were terminated when the balloon temperature reached −60°C and the maximal application duration was 180 seconds. Also, the proximal seal technique was applied to avoid the balloon being vigorously wedged inside the PVs. The use of a 23 mm CB should to avoided because almost all PVs could be isolated by 28 mm CB and a small balloon could become wedged inside the vein.22 Based on the present study data, PV stenosis might not be an issue with the current second-generation CB ablation strategy if the procedure is carefully performed, and routine evaluation of PV stenosis seems not to be necessary.
Cardiac Tamponade
Cardiac tamponade is the most common potentially life-threatening complication associated with AF ablation. In a dedicated worldwide survey, cardiac tamponade was reported to be the most frequent cause of peri-procedural death, accounting for 25% of the deaths, of which 3% occurred later than 30 days post-procedure.1,23,24
We analysed the incidence and characteristics of cardiac tamponade in 5,222 AF ablation procedures in 3,483 patients.25 Cardiac tamponade occurred in 51 procedures/patients, and the incidence was 0.98% per procedure and 1.46% per patient. While there was no significant predictor of this complication, the use of a CB was associated with a lower incidence. The results are in accordance with a randomised prospective study and retrospective registry showing a lower risk of tamponade in CB ablation compared with RF ablation.4,26 The RF ablation requires multiple catheters including mapping catheters and an ablation catheter for the PVI, and the complexity could explain the higher incidence of tamponade. RF ablation of tissue resulted in a reduction in the forces required to perforate the atrial wall; however, treatment with cryoablation did not significantly alter the forces required to induce a perforation, which may explain the lower incidence of tamponade.27 Although the incidence is low in CB ablation procedures, careful manipulation of the CB with a guidewire (Achieve catheter, Medtronic) and careful manoeuvring of the FlexCath sheath (Medtronic) to avoid scratching the atrium are essential to avoid this complication.
Oesophageal Injury and Atrio-oesophageal Fistulae
Atrio-oesophageal fistulae are a rare complication of PVI using not only RF but also CB.1 This is a direct result of the proximity of the oesophagus and the posterior wall of the LA.28,29 In RF ablation, strategies such as modifying energy delivery at the posterior LA close to the oesophagus can minimise the risk. However, in the CB ablation, the posterior LA lesion size cannot specifically be controlled. In the CB ablation, a total of 11 cases of atrio-oesophageal fistulae were reported from more than 120,000 cases worldwide, which is considerably lower than that in RF ablation.30 The balloon inflation time was significantly longer in the patients with atrio-oesophageal fistulae than in those without, and all cases of atrio-oesophageal fistulae occurred in relation to the left PVs.
Since the occurrence of oesophageal fistulae is rare, studies evaluating the impact of oesophageal protection measures have considered the occurrence of endoscopy-detected oesophageal lesions (EDOLs) as the yardstick of the comparison. Despite some limitations of monitoring the luminal oesophageal temperature (LOT), it is suggested as one method of possibly minimising the risk of EDOLs based on the data that EDOLs were more frequently observed in patients with a lower oesophageal temperature during CB ablation.31–33 However, the use of an oesophageal probe for LOT monitoring to avoid oesophageal injury during AF ablation remains unproven in the current guidelines.1
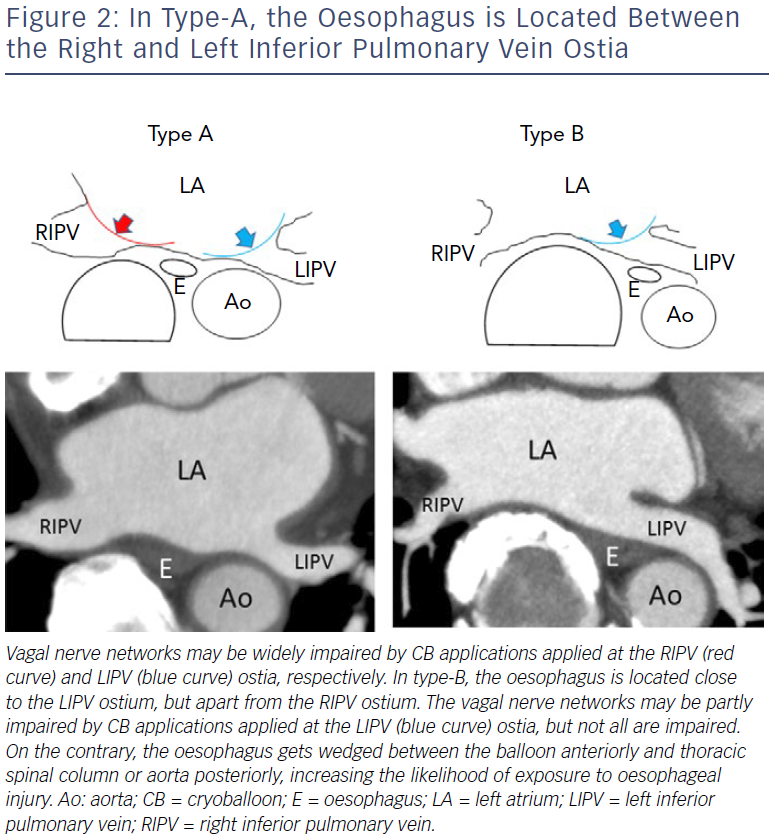
We investigated 104 patients with paroxysmal AF undergoing second-generation cryoballoon ablation with a single 3-minute freeze strategy followed by endoscopy.34 Temperature probes were used in the first 40 patients, but not in the other 64 patients. The incidence of ODELs was significantly higher to monitor LOT in the former rather than the latter group (8/40 versus 1/64; p<0.0001). The use of oesophageal probes was the sole predictor of EDOLs. These data suggest that oesophageal temperature probes themselves may contribute to the thermal injury of the oesophagus. Ahmed et al. reported a 17% incidence of EDOLs after first-generation CB ablation with the use of oesophageal probes, while Guiot et al. reported a 0% incidence without the use of oesophageal probes.35,36 Our results were in accordance with these data. We speculate that, during cryoablation of the left inferior pulmonary vein (LIPV), the oesophagus gets wedged between the balloon anteriorly and thoracic spinal column or aorta posteriorly, increasing the likelihood of exposure to injury (Figure 2).34 We recommend that:
- Freezing at the LIPV should be short.
- Proton-pump inhibiters should be prescribed for 1 month after the procedure to facilitate the healing of oesophageal injury.
- Deep sedation should be avoided.
It has been reported that the use of general anaesthesia increases the risk of oesophageal damage in RF ablation presumably due to reduced motility and reduced deglutination of the oesophagus.37 In the current short-freezing strategy, regardless of the oesophageal temperature monitoring, the risk of oesophageal fistulae seems to be extremely low with CB ablation.
Gastric Hypomotility
The vagal nerve fibres innervating the pyloric sphincter and stomach travel in the left vagal trunk along the anterior aspect of the oesophagus close to the posterior LA and PVs.28 It is well known that injury to the vagal nerve can result in gastric hypomotility characterised by delayed gastric emptying in the absence of an obstructing structural lesion in the stomach manifested as abdominal bloating.38 The incidence is likely underestimated because most asymptomatic patients have not been systemically screened.
As mentioned above, we investigated the incidence of silent gastric hypomotility in 104 patients with paroxysmal AF undergoing second-generation cryoballoon with a single 3-minute freeze strategy followed by endoscopy.33,34 Temperature probes were used in the first 40 patients to monitor the oesophageal temperature, but not in the other 64 patients. The presence of food in the stomach after overnight fasting without obstruction was defined as gastroparesis. The incidence of silent gastric hypomotility was similar between the groups (7/40 versus 11/64; p=0.967), and it was resolved in all patients on repeat endoscopy performed 1–3 months later. The oesophageal temperature was similar in patients with and without silent gastric hypomotility. In multivariate analyses, a shorter distance between the oesophagus and the right inferior PV ostium was the sole predictor of gastric hypomotility. The study clarified that second-generation CB ablation carried a significant risk of silent gastric hypomotility, and the anatomical location of the oesophagus – rather than oesophageal temperature – helped to identify high-risk populations for gastric hypomotility. It is likely that gastric hypomotility frequently occurs immediately after CB ablation but only a few patients become symptomatic.
Another study showed that 3% (n=3) of patients exhibited symptomatic gastric hypomotility despite cryoapplication being terminated when the LOT reached 25°C.39 The symptoms (abdominal bloating and repeated vomiting) manifested 2–5 days post-procedure, after the stomach had time to be filled with food, and abdominal imaging demonstrated marked gastric dilatation with retained food. After fasting for 4–5 days and treatment with panthenol, metoclopramide, and erythromycin, the symptoms were gone and imaging findings showed a complete recovery 7–11 days post-procedure.40 We defined a type-A oesophageal location when the oesophagus was located between the inferior PVs (apart from the LIPV and relatively close to the RIPV) at the inferior PV level, and type-B oesophageal location when the oesophagus was surrounded by the descending aorta, spine, and LIPV (close to the LIPV and apart from the RIPV; Figure 2). The incidence was significantly higher in patients with a type-A rather than a type-B oesophageal location (11.1% versus 1.2%; p=0.083), which was in accordance with the reported incidence of asymptomatic gastric hypomotility (33.3% versus 10.7%).34
The higher incidence of gastric hypomotility with CBs compared with RF ablation may be explained by the differences in the lesion configuration or greater transmural penetration by the CB ablation. We assume that the complex network of nerves located at the anterior aspect of the oesophagus may be widely damaged during ablation of the LIPV and the RIPV in patients whose oesophagus is located between these veins (type-A), increasing the risk of gastric hypomotility (Figure 2). It does not make sense to use LOT monitoring to anticipate this complication. We recommend that:
- The freezing time should be short for the lower PVs, especially in the high-risk population evaluated on pre-procedural imaging.
- Excessive drinking and eating should be avoided post-procedure given the high incidence of asymptomatic gastric hypomotility.
Stroke
Since the incidence of a stroke is low, protective manoeuvres have been considered for silent strokes that were detected on diffusion-weighted MRI on the day after the procedure.41 Possible embolic materials are thrombi, gas bubbles and particulate debris produced during an LA ablation, and silent strokes have been produced experimentally by injecting small-size solid particles or gaseous microbubbles into the brain in animal models.42–44 In RF ablation, the most important step toward reducing symptomatic stroke and transient ischaemic attack rates is to implement uninterrupted anticoagulation into the management of patients undergoing ablation.1 According to guidelines, all AF ablation procedures should be performed under uninterrupted warfarin or dabigatran (class 1, level A).1 However, cryoablation is generally regarded as tissue-friendly and is associated with a significantly lower incidence of thrombus formation compared with RF ablation.18
We investigated the factors associated with the incidence of silent strokes during second-generation CB ablation.45,46 We gave 256 AF patients a brain MRI 1 day after the PVI using second-generation cryoballoons with a single 28 mm balloon and a short-freeze strategy. Silent strokes were detected in 26.5% (n=68) of the patients, and none of the patients reported any neurological symptoms. Reinsertion of a once withdrawn cryoballoon and additional LA mapping with a multielectrode catheter significantly increased the incidence of silent strokes. Transient coronary air embolisms were significantly associated with the incidence of silent strokes.
On the contrary, an uninterrupted anticoagulation regimen,
cryoballoon air removal with extracorporeal balloon inflations, strength of the MRI magnet, internal electrical cardioversion, and touch-up ablation were not associated with the incidence of silent strokes. These results suggest that air embolisms are the main mechanism of silent strokes, and the injected air volume might determine the type of lesion.
These findings underscore the importance of careful de-airing management during procedures using large bore transseptal sheaths in the LA. As well as the strict anticoagulation protocol according to the guidelines1, we recommend:
- Careful sheath management;
- Submerged loading of the catheter into the introducer before sheath insertion to minimise the ingression of air;
- Slow catheter insertion and withdrawal from the sheath because air can be introduced into the transseptal sheath with suction when catheters are removed.
- Reinsertion of a used CB and exchanging catheters with complex geometries via the FlexCath sheath, should be avoided.
Clinical Perspective
- Cryoballoon ablation is associated with several procedural complications and that knowledge is essential for physicians who are involved in the procedure.
- Balloon positioning and freeze dosing are the key to minimise the risk of complication while maintaining the procedure’s efficacy.